DNA; – the blueprint of life
DNA which stands for Deoxyribo Nucleic Acid is the material found in each cell that carries the information required to make up the structure and function of almost all living organisms. Each piece of information carried on a different section of the DNA is referred to as genes. This information (technically called as genetic information) written in DNA is vital for the cellular development and function and is passed on to each successive generation via sexual reproduction.
What DNA does?
Your physical characteristics; from eye color to cholesterol levels are principally determined by proteins in cells. DNA carries all information to produce each of these proteins by instructing the cells on which type of protein to produce, the amounts, when and where.
Where is DNA found?
DNA is found in the center of the cell (known as cell nucleus), organized into structures called chromosomes (Figure 1). Chromosomes are microscopic structures and powerful microscopes are used to observe and explore them. The number of chromosomes found in cells of a particular species remains same while the number differs between species. Human cells consist of 46 chromosomes.
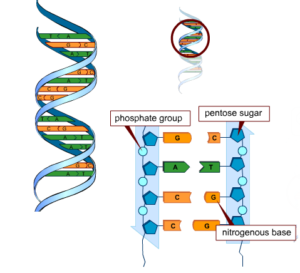
Figure 1: Localization of DNA molecules in the cell nucleus
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/DNA
DNA Structure
DNA molecules are made of small subunits called nucleotides. Hundred to thousand nucleotides are organized to form the DNA structure. The structure of DNA was first discovered by Watson and Crick in 1953, and is described as two long strands or chains joined together to form a ladder like shape that is twisted in the form of a spiral (Figure 2). Nucleotides are represented by the steps of the ladder. A nucleotide is made up of three chemical units; A deoxy-ribose sugar, a nitrogenous base and a phosphate group. Four types of nitrogenous bases can be found in the DNA structure. Based on the nitrogenous base with which the nucleotide is made, they can be divided into four main types; adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine (C). These 4 nucleotide bases are arranged in different orders in each strand of DNA.
The order in which the bases are arranged is very important. It forms a code (genetic code) that directs cells to make certain kinds of proteins. The differences in these proteins give rise to variations in characteristics (eg: hair pattern, eye colour etc) which makes an individual uniquely different from another.
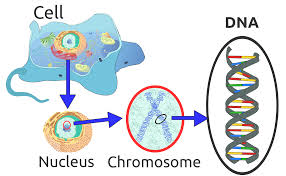
Figure : Structure of the DNA molecule
http://rapguidetoevolution.co.uk/dna
DNA Mutations
Mutations are a natural process that changes the DNA sequence which brings about unique variations in the characteristics of a species. Most of these variations are relatively small and simple, involving only a few bases, for example an Adenine substituted for a thymine.
An organism’s complete set of DNA, including all of its genes is called as the genome. There are found to be more than three million differences (mutations) between genomes of two individuals. These mutations get passed along to the next generation of people. Mutation can either cause positive or negative effects to the individual. Mutations give rise to diseases (eg: cancer) and other health problems (development of the immunological disorders).
DNA Technology
Modern sciences including the understanding of diseases, human behavior, evolution, criminal investigations have been revolutionized by DNA technology. Recombinant DNA technology, DNA fingerprinting and profiling and gene therapy are some novel techniques that are widely used in forensics, environmental sciences, agriculture and medicine. Therefore, DNA research will continue to progress and aid in the understanding of life.
Shavindya Abeygunaratne
